Impedance in a Parallel Circuit
Impedance in an electronic circuit is measured using complex numbers. Below is a drawing of a parallel circuit with the meaning of the electronic symbols.
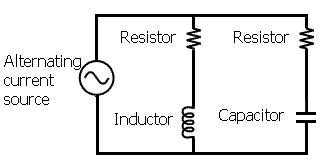
Using the diagram below, if we use the variable r1 for resistance of resistor 1, the variable r2 for resistance of resistor 2,
d1 for the resistance of the inductor,
and c1 for the resistance of the capacitor, the equation for the impedance of the parallel circuit is
Z = (Z1 · Z2) / (Z1 + Z2) where Z1 = r1 + d·i, Z2 = r2 - c·i, and  .
.
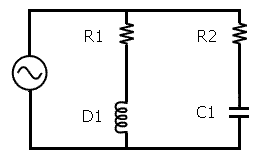
Example
r1 = 10 ohm, r2 = 20 ohm, c1 = 5 ohm, d1 = 10 ohm, so Z1 = 10 + 10·i and Z2 = 20 - 5·i. This means that Z = ((10 + 10i)(20 - 5i))/((10 + 10i) + (20 - 5i)).Using FOIL, (10 + 10i)(20 - 5i) = 200 - 50i + 200i - 50i2 = 200 + 150i - 50·(-1) = 250 + 150i.
(10 + 10i) + (20 - 5i) = (10 + 20) + (10 - 5)i = 30 + 5i.
(250 + 150i) / (30 + 5i) = ((250 + 150i)·(30 - 5i))/((30 + 5i)·(30 - 5i)).
(250 + 150i)·(30 - 5i) = 7500 - 1250i + 4500i - 650i2 = 8150 + 3250i.
(30 + 5i)·(30 - 5i) = 900 - 150i + 150i - 25i2 = 925.
(8150 + 3250i) / 925 = 326/37 + 130/37i.